The impact of user diversity on the willingness to disclose personal information in social network services
Abstract
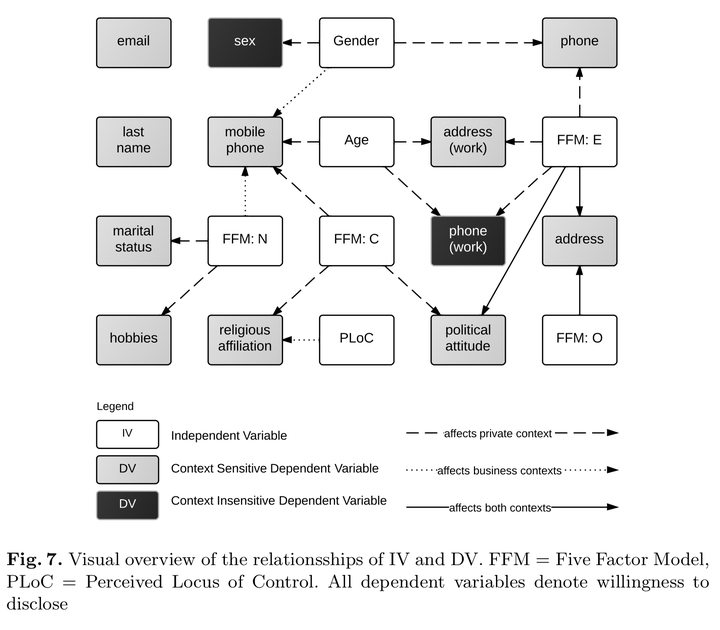
Social media and social network sites (SNS) are a central medium for communication within the Internet. There has never been a faster possibility for information exchange across the globe with a compa- rable range and size of audience. So far, SNS are very popular in private communication. But can other fields of application profit from this role model? To find out more about the comparability of the two contexts (private and business) and to specify transferable design guidelines, we investigated the willingness to disclose private data in both private and business context, knowing that data disclosure is one significant success factor for SNS and communities. Therefore, an exploratory questionnaire study (N = 151) was designed. The focus of the study is based on the question whether there is a difference between the contexts and whether these differences are related to user diversity factors (age, gender, per- ceived locus of control over technology (PLoC), and personality traits according to Five Factor Model (FFM)). First results reveal that there is a significant difference between the two contexts that is hard to explain using only factors of user diversity.